Electric vehicle (EV) charging can sometimes seem like a complex web of terms and acronyms. To navigate the world of EV charging effectively, it’s crucial to understand key concepts like fast vs. slow charging, AC vs. DC charging, Mode 1 vs. Mode 2 vs. Mode 3 vs.
Mode 4 charging, and Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. Level 3 charging. Let’s break them down and explore their relationships.
1. Fast vs. Slow Charging:
-
Fast Charging: Fast charging refers to charging methods that deliver a high amount of electric current to an EV’s battery, significantly reducing charging time. This is typically associated with Direct Current (DC) charging.
-
Slow Charging: Slow charging involves lower electric currents, resulting in longer charging times. It’s often associated with Alternating Current (AC) charging.
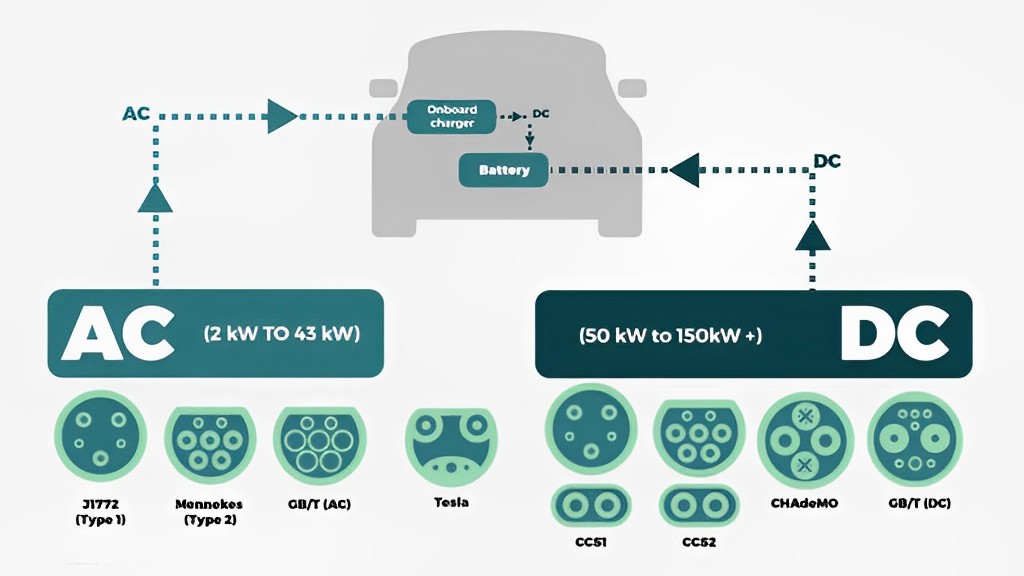
2. AC vs. DC Charging:
-
AC Charging (Alternating Current): AC charging is the method of providing electric power in which the direction of electric current periodically reverses. Most standard home outlets use AC power. Level 1 and Level 2 charging typically use AC power.
-
DC Charging (Direct Current): DC charging involves the continuous flow of electric current in one direction. It’s the preferred method for fast charging (Level 3) as it can rapidly recharge an EV’s battery.
3. Mode 1 vs. Mode 2 vs. Mode 3 vs. Mode 4 Charging:
-
Mode 1 Charging: Mode 1 charging uses a standard electrical outlet with no additional safety features or communication capabilities. It’s the slowest and least secure method.
-
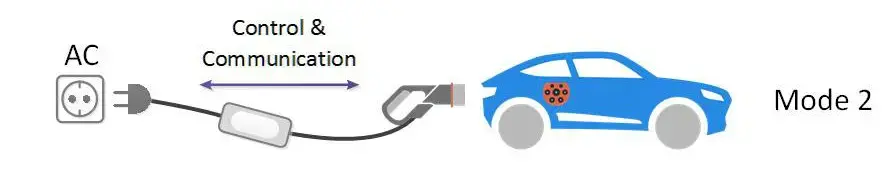
Mode 2 Charging: Mode 2 charging involves a standard outlet but includes added safety features like a residual current device (RCD) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI). It’s safer than Mode 1 but still relatively slow.
-
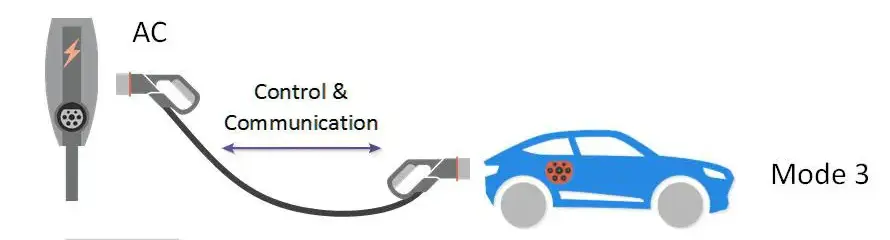
Mode 3 Charging: Mode 3 charging utilizes dedicated charging stations with standardized connectors, communication protocols, and safety features. It’s the safest and most commonly used method for public charging.
-
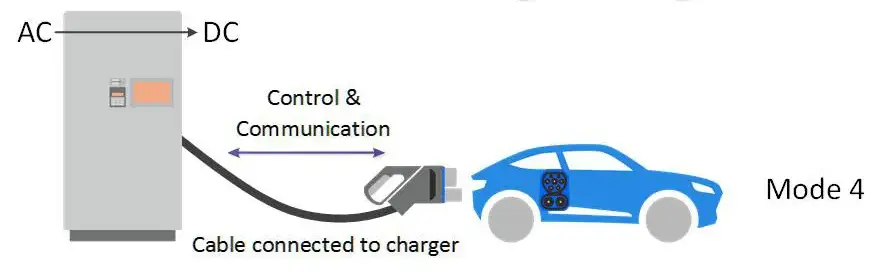
Mode 4 Charging: Mode 4 charging represents fast DC charging with additional communication capabilities, allowing for advanced features like billing and load management.
4. Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. Level 3 Charging:
-
Level 1 Charging: Level 1 charging typically uses a standard 120-volt AC household outlet. It’s the slowest method, adding around 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging.

-
Level 2 Charging: Level 2 charging requires a 240-volt AC charging station. It’s faster, adding approximately 10-30 miles of range per hour.

-
Level 3 Charging: Level 3 charging, also known as fast charging, uses high-powered DC chargers capable of adding around 60-100 miles of range in just 20-30 minutes.
Understanding these charging concepts is essential for EV owners and those considering electric vehicles. They represent different charging speeds, safety features, and levels of convenience.
Fast charging (Level 3 DC) is suitable for long journeys, while slow charging (Level 1 and Level 2 AC) is typically used at home or work for overnight or daily charging.
Mode 3 charging is the preferred method for public charging due to its safety and standardized features, and Mode 4 introduces advanced communication capabilities for fast DC charging.